Port Forwarding Requirements
In order for the controller to be accessible externally, port forwarding must be configured at the router. Port forwarding is a method of mapping an IP address and port on a local subnet to an external port, so that the networked device is accessible over the internet.
In particular, validating a third-party certificate generally requires the controller to be accessible via external port 80. This is the default port for HTTP requests. This external port must be set up to forward traffic to an internal port on the controller that accepts HTTP requests. By default this is internal port 80; however, if required this can be changed in the System Settings.
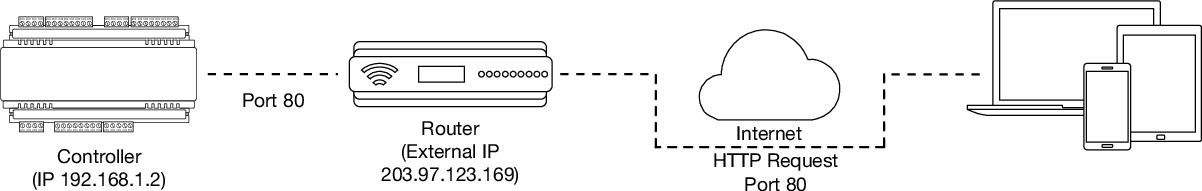
Once this port has been forwarded, the controller will be accessible via the external IP address of the network. In this example, typing 203.97.123.169 into an external web browser will open the controller's web interface.
External access via HTTP is only required in order to validate and install your certificate. Once the certificate has been installed, HTTP access will be disabled because the more secure HTTPS connection is available. Therefore it will no longer be necessary to forward external port 80 to the controller.
Port forwarding is configured from the router's utility interface, which can be accessed by browsing to the router's IP address. Different routers have different interfaces, so it is recommended that you consult the documentation for your router.